Samba 4 Domain Controller Installation auf CentOS 7
Ab Version 4.0 ist Samba in der Lage, als Active Directory (AD) Domain Controller (DC) zu arbeiten. In diesem Tutorial zeige ich Ihnen, wie Sie Samba 4 als Domänencontroller mit Windows 10, CentOS 7 und CentOS 6 Clients konfigurieren.
In diesem Tutorial werde ich Samba 4 aus dem Quellcode kompilieren. Wenn Sie eine Samba 4 RPM-basierte Installation und SELinux-Konfiguration für Samba 4 suchen, finden Sie hier mein neues Samba 4-Tutorial.
Ich werde 3 Systeme, einen CentOS 7 Server und einen Windows 10 Client für die Fernverwaltung, einen CentOS 7 und CentOS 6 Client verwenden.
- 192.168.1.190 Samba4 AD centos7
- 192.168.1.191 Fernverwaltung gewinnen 10
- 192.168.1.22 – Client Authentifizierung – centos 7
- 192.168.1.192 – Client Authentifizierung – centos 6
Installation von Samba 4
192.168.1.190 Samba4 AD centos 7
Basis ist ein CentOS 7 mit minimaler Installation und deaktiviertem SELinux.
[root@samba4 ~]# sestatus SELinux status: disabled [root@samba4 ~]#
Mache einen Eintrag in der Datei /etc/hosts.
[root@samba4 ~]# cat /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.1.190 samba4.sunil.cc samba4 [root@samba4 ~]#
Installieren Sie den epel repo.
[root@samba4 ~]# yum install epel-release -y
Installieren Sie alle Pakete, die Sie für die Kompilierung von samba4 benötigen.
[root@samba4 ~]# yum install perl gcc libacl-devel libblkid-devel gnutls-devel readline-devel python-devel gdb pkgconfig krb5-workstation zlib-devel setroubleshoot-server libaio-devel setroubleshoot-plugins\ policycoreutils-python libsemanage-python setools-libs-python setools-libs popt-devel libpcap-devel sqlite-devel libidn-devel libxml2-devel libacl-devel libsepol-devel libattr-devel keyutils-libs-devel\ cyrus-sasl-devel cups-devel bind-utils libxslt docbook-style-xsl openldap-devel pam-devel bzip2 vim wget -y
Jetzt Samba4-Paket herunterladen. Ich benutze Samba-4.6.0, das ist der neueste Stand bei diesem Setup.
[root@samba4 ~]# wget https://download.samba.org/pub/samba/stable/samba-4.6.0.tar.gz
Jetzt können Sie samba4 installieren.
[root@samba4 ~]# tar -zxvf samba-4.6.0.tar.gz [root@samba4 ~]# cd samba-4.6.0 [root@samba4 samba-4.6.0]# ./configure --enable-debug --enable-selftest --with-ads --with-systemd --with-winbind [root@samba4 samba-4.6.0]# make && make install
Die Installation dauert je nach Systemgeschwindigkeit ca. 10 Minuten.
Nun werden wir die Domain-Bereitstellung vornehmen.
[root@samba4 samba]# samba-tool domain provision --use-rfc2307 --interactive
Realm [SUNIL.CC]:
Domain [SUNIL]:
Server Role (dc, member, standalone) [dc]: dc
DNS backend (SAMBA_INTERNAL, BIND9_FLATFILE, BIND9_DLZ, NONE) [SAMBA_INTERNAL]:
DNS forwarder IP address (write 'none' to disable forwarding) [4.2.2.1]:
Administrator password:
Retype password:
Looking up IPv4 addresses
Looking up IPv6 addresses
No IPv6 address will be assigned
Setting up share.ldb
Setting up secrets.ldb
Setting up the registry
Setting up the privileges database
Setting up idmap db
Setting up SAM db
Setting up sam.ldb partitions and settings
Setting up sam.ldb rootDSE
Pre-loading the Samba 4 and AD schema
Adding DomainDN: DC=sunil,DC=cc
Adding configuration container
Setting up sam.ldb schema
Setting up sam.ldb configuration data
Setting up display specifiers
Modifying display specifiers
Adding users container
Modifying users container
Adding computers container
Modifying computers container
Setting up sam.ldb data
Setting up well known security principals
Setting up sam.ldb users and groups
ERROR(ldb): uncaught exception - operations error at ../source4/dsdb/samdb/ldb_modules/password_hash.c:2820
File "/usr/local/samba/lib64/python2.7/site-packages/samba/netcmd/__init__.py", line 176, in _run
return self.run(*args, **kwargs)
File "/usr/local/samba/lib64/python2.7/site-packages/samba/netcmd/domain.py", line 471, in run
nosync=ldap_backend_nosync, ldap_dryrun_mode=ldap_dryrun_mode)
File "/usr/local/samba/lib64/python2.7/site-packages/samba/provision/__init__.py", line 2175, in provision
skip_sysvolacl=skip_sysvolacl)
File "/usr/local/samba/lib64/python2.7/site-packages/samba/provision/__init__.py", line 1787, in provision_fill
next_rid=next_rid, dc_rid=dc_rid)
File "/usr/local/samba/lib64/python2.7/site-packages/samba/provision/__init__.py", line 1447, in fill_samdb
"KRBTGTPASS_B64": b64encode(krbtgtpass.encode('utf-16-le'))
File "/usr/local/samba/lib64/python2.7/site-packages/samba/provision/common.py", line 55, in setup_add_ldif
ldb.add_ldif(data, controls)
File "/usr/local/samba/lib64/python2.7/site-packages/samba/__init__.py", line 225, in add_ldif
self.add(msg, controls)
[root@samba4 samba]#
Es wird einige Fehler geben, wenn wir die Bereitstellung der Domain vornehmen.
Um sie zu beheben, kommentieren Sie bitte die folgende Zeile in /etc/krb5.conf aus.
-------- #includedir /etc/krb5.conf.d/ --------
Führen Sie die Domänenbereitstellung erneut durch und die Domäne wird nun fehlerfrei erstellt.
[root@samba4 etc]# samba-tool domain provision --use-rfc2307 --interactive Realm [SUNIL.CC]: Domain [SUNIL]: Server Role (dc, member, standalone) [dc]: DNS backend (SAMBA_INTERNAL, BIND9_FLATFILE, BIND9_DLZ, NONE) [SAMBA_INTERNAL]: DNS forwarder IP address (write 'none' to disable forwarding) [4.2.2.1]: Administrator password: Retype password: Looking up IPv4 addresses Looking up IPv6 addresses No IPv6 address will be assigned Setting up secrets.ldb Setting up the registry Setting up the privileges database Setting up idmap db Setting up SAM db Setting up sam.ldb partitions and settings Setting up sam.ldb rootDSE Pre-loading the Samba 4 and AD schema Adding DomainDN: DC=sunil,DC=cc Adding configuration container Setting up sam.ldb schema Setting up sam.ldb configuration data Setting up display specifiers Modifying display specifiers Adding users container Modifying users container Adding computers container Modifying computers container Setting up sam.ldb data Setting up well known security principals Setting up sam.ldb users and groups Setting up self join Adding DNS accounts Creating CN=MicrosoftDNS,CN=System,DC=sunil,DC=cc Creating DomainDnsZones and ForestDnsZones partitions Populating DomainDnsZones and ForestDnsZones partitions Setting up sam.ldb rootDSE marking as synchronized Fixing provision GUIDs A Kerberos configuration suitable for Samba AD has been generated at /usr/local/samba/private/krb5.conf Setting up fake yp server settings Once the above files are installed, your Samba4 server will be ready to use Server Role: active directory domain controller Hostname: samba4 NetBIOS Domain: SUNIL DNS Domain: sunil.cc DOMAIN SID: S-1-5-21-2936486394-2075362935-551615353 [root@samba4 etc]#
Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Ports in der Firewall offen sind.
[root@samba4 etc]#firewall-cmd --add-port=53/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=53/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=88/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=88/udp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=135/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=137-138/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=139/tcp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=389/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=389/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=445/tcp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=464/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=464/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=636/tcp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=1024-5000/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=3268-3269/tcp --permanent [root@samba4 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
Erstellen Sie ein Startskript, um den Dienst während des Neustarts automatisch zu starten.
[root@samba4 ~]# cat /etc/systemd/system/samba.service [Unit] Description= Samba 4 Active Directory After=syslog.target After=network.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/usr/local/samba/var/run/samba.pid ExecStart=/usr/local/samba/sbin/samba [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target [root@samba4 ~]# [root@samba4 ~]# systemctl enable samba Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/samba.service to /etc/systemd/system/samba.service. [root@samba4 ~]# systemctl start samba
Hinzufügen des Windows-Rechners zur Domäne
192.168.1.191 Fernverwaltung gewinnen 10
Stellen Sie sicher, dass der Host mit einer statischen IP-Adresse hinzugefügt wird.
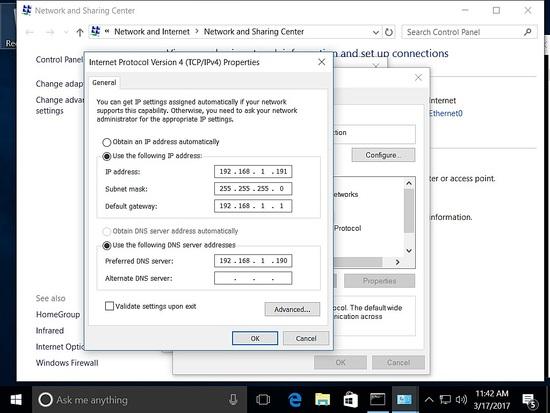
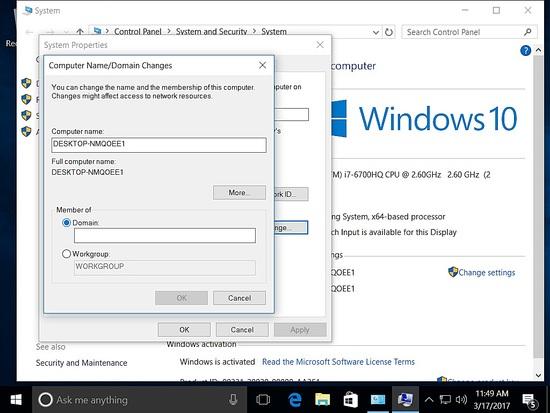
Hinzufügen des Hosts zur Domäne.
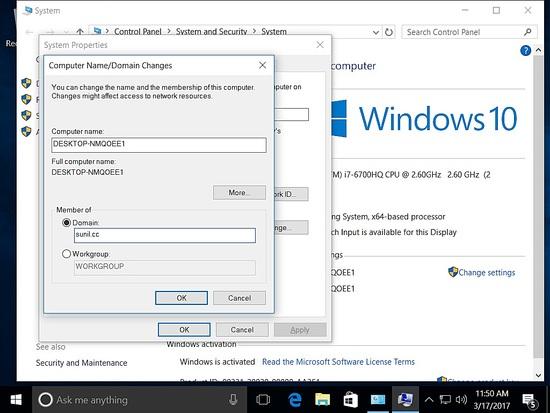

Um Samba4 von Windows aus zu verwalten, benötigen wir die Microsoft Remote Server Tools (RSAT).
Die Wiki-Seite hat die Links https://wiki.samba.org/index.php/Installing_RSAT
Installation des RSAT-Tools unter Windows 10
Starten Sie das Installationsprogramm.
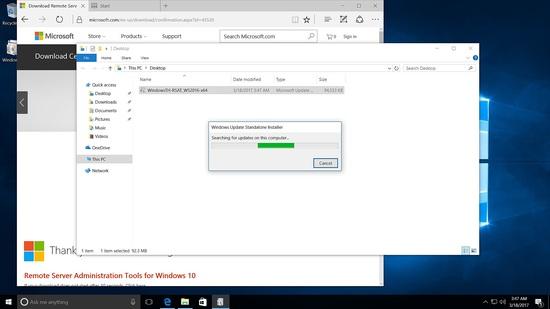
Nach dem Neustart gehen Sie zur Ausführung und geben Sie Folgendes ein dsa.msc
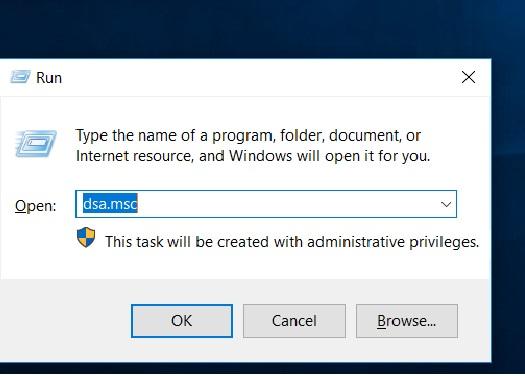
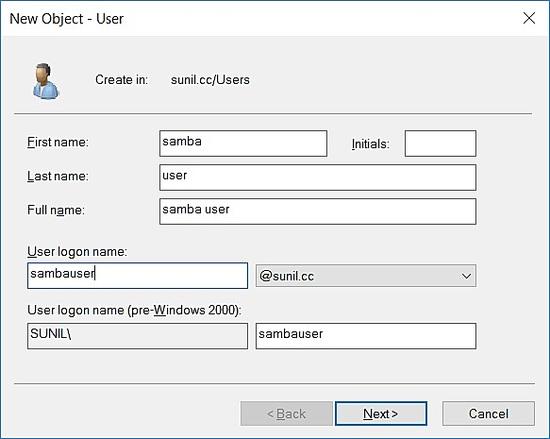
Klicken Sie auf sunil.cc Domain und klicken Sie mit der rechten Maustaste auf neu -> Benutzer.

Anlegen eines Testbenutzers.

Client-Authentifizierung mit Samba 4 auf CentOS 7
192.168.1.22 – Client-Authentifizierung auf CentOS 7
Installation von Paketen:
[root@centos7 ~]# yum -y install realmd sssd oddjob oddjob-mkhomedir adcli samba-common
Überprüfen Sie die Konnektivität mit samba4:
[root@centos7 ~]# realm discover SUNIL.CC sunil.cc type: kerberos realm-name: SUNIL.CC domain-name: sunil.cc configured: kerberos-member server-software: active-directory client-software: sssd required-package: oddjob required-package: oddjob-mkhomedir required-package: sssd required-package: adcli required-package: samba-common-tools login-formats: %U login-policy: allow-realm-logins [root@centos7 ~]#
Beitritt zur Domäne.
[root@centos7 ~]# realm join SUNIL.CC Password for Administrator: [root@centos7 ~]#
Überprüfen Sie, ob wir den Benutzer von samba4 bekommen können.
[root@centos7 ~]# id SUNIL\\testuser uid=1570001104(testuser@sunil.cc) gid=1570000513(domain users@sunil.cc) groups=1570000513(domain users@sunil.cc) [root@centos7 ~]#
Konfigurieren Sie sssd.
[root@centos7 ~]# cat /etc/sssd/sssd.conf [sssd] domains = sunil.cc config_file_version = 2 services = nss, pam [domain/sunil.cc] ad_domain = sunil.cc krb5_realm = SUNIL.CC realmd_tags = manages-system joined-with-samba cache_credentials = True id_provider = ad krb5_store_password_if_offline = True default_shell = /bin/bash ldap_id_mapping = True use_fully_qualified_names = True fallback_homedir = /home/%u@%d access_provider = ad [root@centos7 ~]#
Starten Sie sssd neu.
[root@centos7 ~]# systemctl restart sssd [root@centos7 ~]# systemctl enable sssd
Überprüfen Sie den Benutzer.
[root@centos7 ~]# id sambauser@sunil.cc uid=1570001105(sambauser@sunil.cc) gid=1570000513(domain users@sunil.cc) groups=1570000513(domain users@sunil.cc),1570000512(domain admins@sunil.cc),1570000572(denied rodc password replication group@sunil.cc) [root@centos7 ~]#
Um den Benutzer ohne Domänennamen zu erhalten.
[root@centos7 ~]# vim /etc/sssd/sssd.conf ----------- ------------ use_fully_qualified_names = False ----------- -----------
Starten Sie sssd neu und überprüfen Sie den Befehl id.
[root@centos7 ~]# systemctl restart sssd [root@centos7 ~]# id sambauser uid=1570001105(sambauser) gid=1570000513(domain users) groups=1570000513(domain users),1570000512(domain admins),1570000572(denied rodc password replication group) [root@centos7 ~]#
Client-Authentifizierung mit Samba 4 auf CentOS 6
192.168.1.192 – Client-Authentifizierung auf CentOS 6.
Installation von Paketen.
[root@centos6 db]# yum install pam pam_ldap pam_krb5 sssd sssd-ldap sssd-common authconfig oddjob oddjob-mkhomedir openldap openldap-clients krb5-workstation adcli -y
Ändere die Kerberos-Konfigurationsdatei.
[root@centos6 db]# cat /etc/krb5.conf
[logging]
default = FILE:/var/log/krb5libs.log
kdc = FILE:/var/log/krb5kdc.log
admin_server = FILE:/var/log/kadmind.log
[libdefaults]
default_realm = SUNIL.CC
dns_lookup_realm = false
dns_lookup_kdc = false
ticket_lifetime = 24h
renew_lifetime = 7d
forwardable = true
[realms]
SUNIL.CC = {
kdc = samba4.sunil.cc
admin_server = samba4.sunil.cc
}
[domain_realm]
.sunil.cc = SUNIL.CC
sunil.cc = SUNIL.CC
[root@centos6 db]#
Wir werden den Befehl adcli verwenden, um der Domäne beizutreten.
[root@centos6 db]# adcli info sunil.cc [domain] domain-name = sunil.cc domain-short = SUNIL domain-forest = sunil.cc domain-controller = samba4.sunil.cc domain-controller-site = Default-First-Site-Name domain-controller-flags = pdc gc ldap ds kdc timeserv closest writable good-timeserv full-secret domain-controller-usable = yes domain-controllers = samba4.sunil.cc [computer] computer-site = Default-First-Site-Name [root@centos6 db]# [root@centos6 db]# adcli join sunil.cc Password for Administrator@SUNIL.CC: [root@centos6 db]#
Stellen Sie sicher, dass das Kerberos-Ticket erstellt ist.
[root@centos6 db]# klist -ke
Konfigurieren Sie die Authentifizierung.
[root@centos6 db]# authconfig --enablesssd --enablesssdauth --enablemkhomedir --update
Ändere jetzt die sssd-Konfiguration, um die Authentifizierung durchzuführen.
[root@centos6 db]# cat /etc/sssd/sssd.conf [sssd] services = nss, pam, ssh, autofs config_file_version = 2 domains = sunil.cc [domain/sunil.cc] id_provider = ad # Uncomment if service discovery is not working # ad_server = server.win.example.com default_shell = /bin/bash fallback_homedir = /home/%u [root@centos6 db]#
Starten Sie den sssd-Dienst neu.
[root@centos6 db]# chkconfig sssd on [root@centos6 db]# service sssd restart Stopping sssd: [ OK ] Starting sssd: [ OK ] [root@centos6 db]#
Benutzer validieren.
[root@centos6 db]# id sambauser uid=1570001105(sambauser) gid=1570000513(domain users) groups=1570000513(domain users),1570000512(domain admins),1570000572(denied rodc password replication group) [root@centos6 db]#