Samba 4 mit Active Directory auf CentOS 7 – rpm basierte Installation mit Share-Unterstützung
In diesem Tutorial werde ich SAMBA mit AD Unterstützung unter Verwendung von Paketen aus dem Wing Repository installieren. Weiterhin werde ich zeigen wie man eine Samba-Freigabe erstellt. Es wird ein CentOS 7-Server mit einer minimalen Installation als Basis verwendet mit aktiviertem SELinux.
Vorbereiten des CentOS 7 Servers
Überprüfen Sie den SELinux-Status.
[root@samba4 ~]# sestatus SELinux status: enabled SELinuxfs mount: /sys/fs/selinux SELinux root directory: /etc/selinux Loaded policy name: targeted Current mode: enforcing Mode from config file: enforcing Policy MLS status: enabled Policy deny_unknown status: allowed Max kernel policy version: 28 [root@samba4 ~]#
Machen Sie einen Eintrag in der Hostdatei mit der Server-IP-Adresse, gefolgt vom vollständigen (fqdn) Hostnamen und dann dem lokalen Teil des Hostnamens.
[root@samba4 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.1.190 samba4.sunil.cc samba4
[root@samba4 ~]#
Installieren Sie das Epel CentOS-Repository.
[root@samba4 ~]# yum install epel-release -y
Installieren Sie die Basispakete.
[root@samba4 ~]# yum install vim wget authconfig krb5-workstation -y
Montieren Sie nun das Flügel-Repo.
[root@samba4 ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ [root@samba4 yum.repos.d]# wget http://wing-net.ddo.jp/wing/7/EL7.wing.repo [root@samba4 yum.repos.d]# sed -i 's@enabled=0@enabled=1@g' /etc/yum.repos.d/EL7.wing.repo [root@samba4 yum.repos.d]# yum clean all Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Cleaning repos: base extras updates wing wing-source Cleaning up everything Cleaning up list of fastest mirrors [root@samba4 yum.repos.d]#
Samba 4 auf CentOS 7 installieren
Installation der Samba4-Pakete aus dem Wing-Repository mit yum.
[root@samba4 yum.repos.d]# yum install -y samba45 samba45-winbind-clients samba45-winbind samba45-client\ samba45-dc samba45-pidl samba45-python samba45-winbind-krb5-locator perl-Parse-Yapp\ perl-Test-Base python2-crypto samba45-common-tools
Entfernen Sie diese Dateien.
[root@samba4 ~]# rm -rf /etc/krb5.conf [root@samba4 ~]# rm -rf /etc/samba/smb.conf
Samba 4 Konfiguration
Nun werden wir die Domain-Bereitstellung vornehmen.
[root@samba4 ~]# samba-tool domain provision --use-rfc2307 --interactive Realm [SUNIL.CC]: Domain [SUNIL]: Server Role (dc, member, standalone) [dc]: DNS backend (SAMBA_INTERNAL, BIND9_FLATFILE, BIND9_DLZ, NONE) [SAMBA_INTERNAL]: DNS forwarder IP address (write 'none' to disable forwarding) [4.2.2.1]: Administrator password: Retype password: Looking up IPv4 addresses Looking up IPv6 addresses No IPv6 address will be assigned Setting up secrets.ldb Setting up the registry Setting up the privileges database Setting up idmap db Setting up SAM db Setting up sam.ldb partitions and settings Setting up sam.ldb rootDSE Pre-loading the Samba 4 and AD schema Adding DomainDN: DC=sunil,DC=cc Adding configuration container Setting up sam.ldb schema Setting up sam.ldb configuration data Setting up display specifiers Modifying display specifiers Adding users container Modifying users container Adding computers container Modifying computers container Setting up sam.ldb data Setting up well known security principals Setting up sam.ldb users and groups Setting up self join Adding DNS accounts Creating CN=MicrosoftDNS,CN=System,DC=sunil,DC=cc Creating DomainDnsZones and ForestDnsZones partitions Populating DomainDnsZones and ForestDnsZones partitions Setting up sam.ldb rootDSE marking as synchronized Fixing provision GUIDs A Kerberos configuration suitable for Samba 4 has been generated at /var/lib/samba/private/krb5.conf Setting up fake yp server settings Once the above files are installed, your Samba4 server will be ready to use Server Role: active directory domain controller Hostname: samba4 NetBIOS Domain: SUNIL DNS Domain: sunil.cc DOMAIN SID: S-1-5-21-1578983437-3114190590-2362936743 [root@samba4 etc]#
Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Ports in der Firewall geöffnet sind.
[root@samba4 etc]#firewall-cmd --add-port=53/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=53/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=88/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=88/udp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=135/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=137-138/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=139/tcp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=389/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=389/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=445/tcp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=464/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=464/udp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=636/tcp --permanent; \ firewall-cmd --add-port=1024-3500/tcp --permanent;firewall-cmd --add-port=3268-3269/tcp --permanent [root@samba4 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
Das Paket enthält das Initskript nicht, wir werden es jetzt hinzufügen.
[root@samba4 ~]# cat /etc/systemd/system/samba.service [Unit] Description= Samba 4 Active Directory After=syslog.target After=network.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/var/run/samba.pid ExecStart=/usr/sbin/samba [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target [root@samba4 ~]# [root@samba4 ~]# systemctl enable samba Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/samba.service to /etc/systemd/system/samba.service. [root@samba4 ~]# systemctl restart samba
Erstellung der Samba-Freigabe mit Windows ACL-Unterstützung
Wir müssen die erweiterte ACL für samba4 konfigurieren. Füge folgendes in der Datei smb.conf unter global hinzu.
[root@samba4 ~]# cat /etc/samba/smb.conf
# Global parameters
[global]
------------
-------------
vfs objects = acl_xattr
map acl inherit = yes
store dos attributes = yes
------------
-------------
[root@samba4 ~]#
Starten Sie nun den Samba-Dienst neu.
[root@samba4 ~]# systemctl restart samba
Nur Benutzer und Gruppen, denen das SeDiskOperatorPrivilege-Privileg gewährt wurde, können Freigabeberechtigungen konfigurieren.
[root@samba4 ~]# net rpc rights grant "SUNIL\Domain Admins" SeDiskOperatorPrivilege -U "USER\administrator" Enter USER\administrator's password: Successfully granted rights. [root@samba4 ~]#
Bevor wir die Freigabe erstellen, müssen wir sicherstellen, dass sich der samba4-Server mit sich selbst authentifiziert.
Wir können die übliche Methode nicht anwenden, da es nicht funktioniert, da das bestehende Paket vom Flügel mit den von RedHat gelieferten Paketen kollidiert, wir können sssd hier nicht verwenden. winbind wird verwendet, um dies zum Laufen zu bringen.
Bitte verwenden Sie die folgende Methode. Dies ist erforderlich, um die Samba-Freigabe mit bestimmten Berechtigungen zu erstellen.
Installieren Sie das folgende Paket.
[root@samba4 ~]#yum -y install authconfig-gtk*
Führen Sie den Befehl aus.
[root@samba4 yum.repos.d]# authconfig-tui
Bitte wählen Sie die Windbindung aus, folgen Sie den nächsten Schritten.
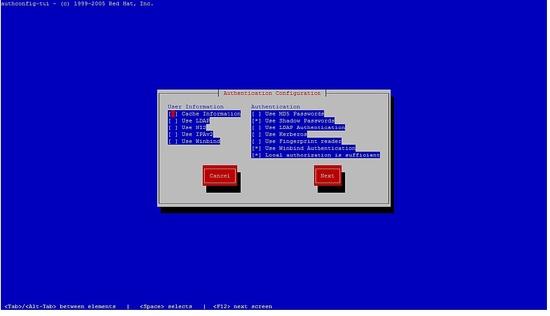
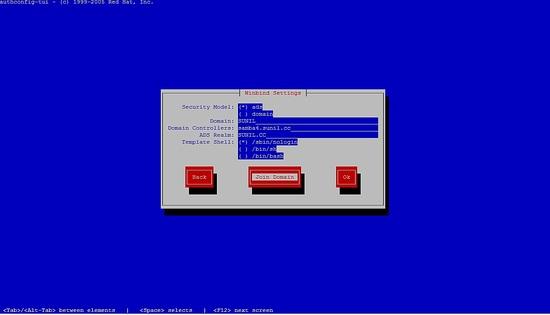
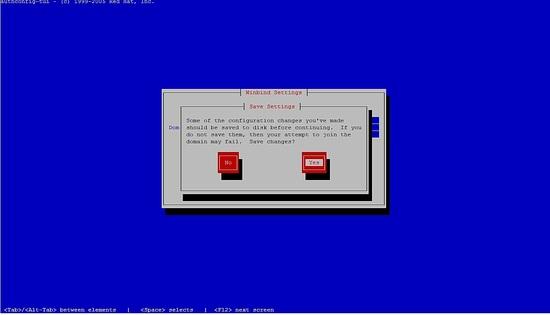
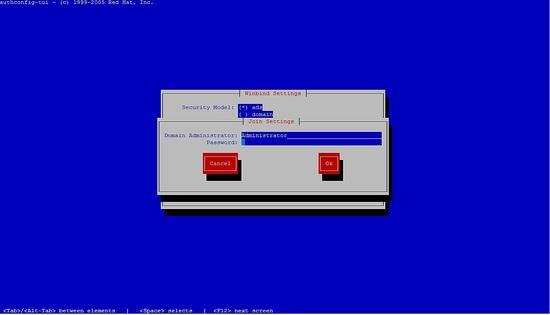
Sie können das Passwort nicht eingeben, drücken Sie einfach auf OK.
Dann kommentieren Sie Zeilen in /etc/samba/smb.conf aus und starten Sie den Samba-Dienst neu.
Ihre Konfiguration sollte wie folgt aussehen:
[root@samba4 ~]# cat /etc/samba/smb.conf
# Global parameters
[global]
#--authconfig--start-line--
# Generated by authconfig on 2017/05/26 17:23:04
# DO NOT EDIT THIS SECTION (delimited by --start-line--/--end-line--)
# Any modification may be deleted or altered by authconfig in future
# workgroup = SUNIL
# password server = samba4.sunil.cc
# realm = SUNIL.CC
# security = ads
# idmap config * : range = 16777216-33554431
# template shell = /sbin/nologin
# kerberos method = secrets only
# winbind use default domain = false
# winbind offline logon = false
#--authconfig--end-line--
netbios name = SAMBA4
realm = SUNIL.CC
workgroup = SUNIL
dns forwarder = 4.2.2.1
server role = active directory domain controller
idmap_ldb:use rfc2307 = yes
vfs objects = acl_xattr
map acl inherit = yes
store dos attributes = yes
[netlogon]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol/sunil.cc/scripts
read only = No
[sysvol]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol
read only = No
[root@samba4 ~]#
[root@samba4 ~]# systemctl restart samba
Überprüfen Sie, ob wir die Benutzer und Gruppen besetzen können:
[root@samba4 ~]# wbinfo -u SUNIL\administrator SUNIL\sambauser SUNIL\testuser SUNIL\krbtgt SUNIL\guest [root@samba4 ~]# wbinfo -g SUNIL\cert publishers SUNIL\ras and ias servers SUNIL\allowed rodc password replication group SUNIL\denied rodc password replication group SUNIL\dnsadmins SUNIL\enterprise read-only domain controllers SUNIL\domain admins SUNIL\domain users SUNIL\domain guests SUNIL\domain computers SUNIL\domain controllers SUNIL\schema admins SUNIL\enterprise admins SUNIL\group policy creator owners SUNIL\read-only domain controllers SUNIL\dnsupdateproxy [root@samba4 ~]#
Ändern Sie die Zeilen in der nsswitch.conf:
[root@samba4 ~]# cat /etc/nsswitch.conf ---------- --------- passwd: files winbind shadow: files winbind group: files winbind hosts: files dns wins services: files winbind netgroup: files winbind --------- ----------
Überprüfen Sie nun, ob wir den Benutzernamen mit dem Befehl id erhalten können:
[root@samba4 ~]# id testuser uid=3000019(SUNIL\testuser) gid=100(users) groups=100(users),3000019(SUNIL\testuser),3000009(BUILTIN\users) [root@samba4 ~]#
Erstellen einer Samba-Freigabe
Ich werde zwei Freigaben erstellen, eine, die nur für Testbenutzer zugänglich ist und die andere, die für alle Benutzer der Domänenbenutzergruppe zugänglich ist.
Die Freigabe, auf die der Tester zugreifen kann, wird als Testshare bezeichnet.
Die Freigabe, auf die alle Benutzer Zugriff haben, wird als Commonshare bezeichnet.
[root@samba4 ~]# mkdir /testshare [root@samba4 ~]# mkdir /commonshare [root@samba4 ~]# chmod 770 /testshare [root@samba4 ~]# chmod 770 /commonshare [root@samba4 ~]# chown -R root:testuser /testshare [root@samba4 ~]# chown -R root:"Domain Users" /commonshare
Füge nun die Einträge in der smb.conf hinzu.
[root@samba4 ~]# cat /etc/samba/smb.conf
# Global parameters
[global]
netbios name = SAMBA4
realm = SUNIL.CC
workgroup = SUNIL
dns forwarder = 4.2.2.1
server role = active directory domain controller
idmap_ldb:use rfc2307 = yes
vfs objects = acl_xattr
map acl inherit = yes
store dos attributes = yes
[netlogon]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol/sunil.cc/scripts
read only = No
[sysvol]
path = /var/lib/samba/sysvol
read only = No
[TestShare]
comment = Test share accessible by testuser
path = /testshare
valid users = SUNIL\testuser
writable = yes
read only = no
force create mode = 0660
create mask = 0770
directory mask = 0770
force directory mode = 0770
access based share enum = yes
hide unreadable = yes
[CommonShare]
comment = Accessible by all the users
path = /commonshare
valid users = "@SUNIL\Domain Users"
writable = yes
read only = no
force create mode = 0660
create mask = 0777
directory mask = 0777
force directory mode = 0770
access based share enum = yes
hide unreadable = yes
[root@samba4 ~]#
Starten Sie den Samba-Dienst neu.
[root@samba4 ~]# systemctl restart samba
Greifen Sie als Testbenutzer auf die Samba-Freigabe zu.
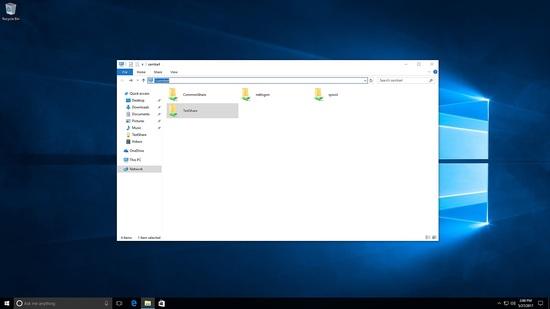
Hier sehen Sie, dass sowohl Testshare als auch Commonshare sichtbar sind.
Geprüftes Erstellen von Dateien und Ordnern unter test share.
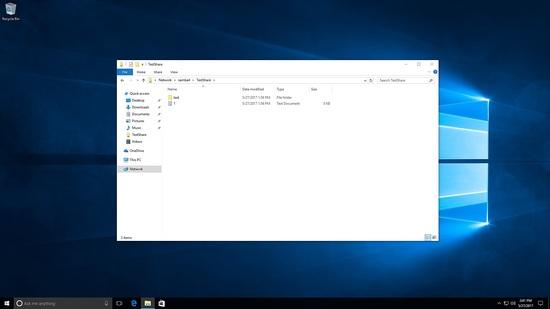
[root@samba4 /]# cd /testshare/ [root@samba4 testshare]# ls -l total 8 -rwxrwx---+ 1 SUNIL\testuser users 0 May 27 22:56 1.txt drwxrwx---+ 2 SUNIL\testuser users 6 May 27 22:56 test [root@samba4 testshare]#
Jetzt melde ich mich mit einem anderen Benutzer an, nur Commonshare ist sichtbar:
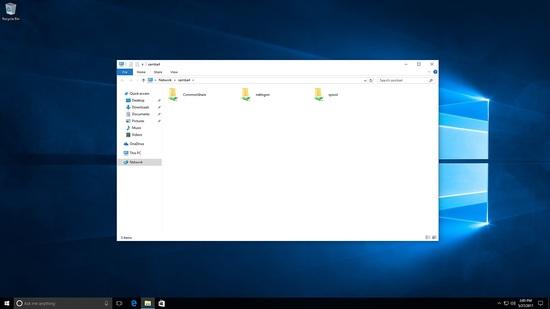
Erstellen von Dateien unter Commonshare.
[root@samba4 commonshare]# ls -l total 8 drwxrwxrwx+ 2 SUNIL\testuser users 6 May 27 23:02 test drwxrwxrwx+ 2 SUNIL\sambauser users 6 May 27 23:07 test2 [root@samba4 commonshare]#
So erstellen wir Freigaben unter Samba 4.